Pecan (https://pypi.python.org/pypi/pecan): It is another entry of Python web framework. It is a lean, light weight solution in order to implement web framework in comparison with home-grown WSGI framework. There are some projects in OpenStack now that are using Pecan such as Ceilometer, Ironic, etc.
The reason why changing to python Pecan is essential is below:
https://specs.openstack.org/openstack/neutron-specs/specs/kilo/pecan-switch.html
I am not going to details what is inside pecan but you can search for that easily. In this example, let’s have something interesting into how to use pecan and mod_wsgi to implement a web server – based service.
The question is why we need mod_wsgi? What is the story of implementing web server – based service here relating to cloud?
First of all, the case study here is not about OpenStack infrastructure but it is about how to create a service that deploys cloud app onto OpenStack based cloud environment. Imagine that, a client will use GUI and by clicking some options on the GUI, he/she then has cloud app running on top of OpenStack cloud. Therefore you need to have a service A that will help you to take the requests from clients then execute the actions of deploying cloud app. Then it will send the notifications to service B that then executes notification actions such as alarm-creation, alarm-sending, etc. In the architect of pattern software architect, we can think about it as Publisher-Subcriber model. In order to make service A (Publisher) light-weight, easy-to-interoperate, one solution is making it running as web server using apache. In this case, service A is written in Python, uses Pecan for python web framework and Apache will wrap service A and run it as web server by using Apache mod_wsgi.
Apache mod_wsgi: It is a module that implements a simple to use Apache module which hosts the Python application that supports Python WSGI interface. Of course in our environment of OpenStack, the alternative Pecan truly supports WSGI interface. Therefore, it is a relevant approach in this case.
Note that, in Debian-base distros like Ubuntu, It is called Apache, in Redhat-based distros (Centos, Fedora, Redhat), it is called httpd.
So, here we go:
- In my example, I use ubuntu 16.04 Xenial Xerus and create virtualenv for running this test bed.
-
Firstly, you should install mod_wsgi:
apt-get install libapache2-mod-wsgi
- Then, using the Apache virtual host to host the domain where Python pecan application runs. I create my own file called pecan_test.conf, you can change it as whatever name you would like
/etc/apache2/sites-available/pecan_test.conf:
Listen 127.0.0.1:8080
ServerName pecan_test
WSGIDaemonProcess pecan_test threads=5 user=tuan
WSGIPassAuthorization On
WSGIScriptAlias / /var/www/pecan_test/app.wsgi
WSGIProcessgroup pecan_test
WSGIApplicationgroup %{GLOBAL}
Order deny,allow
Allow from all
You can see that, the WSGIScriptAlias will point to the app.wsgi that points to the config file of a python pecan application. To understand the pecan usage, it is your homework:)
/var/www/pecan_test/app.wsgi:
from pecan.deploy import deploy
application = deploy('/var/www/pecan_test/config.py')
/var/www/pecan_test/config.py:
#Server Specific Configurations
server = {
'port': '8080',
'host': '0.0.0.0'
}
#Pecan Application Configurations
app = {
'root': 'pecanrest.controllers.root.RootController',
'modules': ['pecanrest'],
'static_root': '%(confdir)s/public',
'template_path': '%(confdir)s/pecanrest/templates',
'debug': True,
'errors': {
404: '/error/404',
'force_dict': True
}
}
You can see that, in the ‘root’ keyword, the code where pecan python app uses in under pecanrest/controllers/root folder. You can follow the below link to see how to use pecan in a simple example:
http://www.giantflyingsaucer.com/blog/?p=4834
Finally, when you have all the thing set up, you should enable mod_wsgi:
(pecan_test) tuan@tuan-luong:/etc/apache2/sites-available$ sudo a2enmod wsgi
Enabling module wsgi.
To activate the new configuration, you need to run:
service apache2 restart
Then restarting apache2:
service apache2 restart
Now, checking the result:
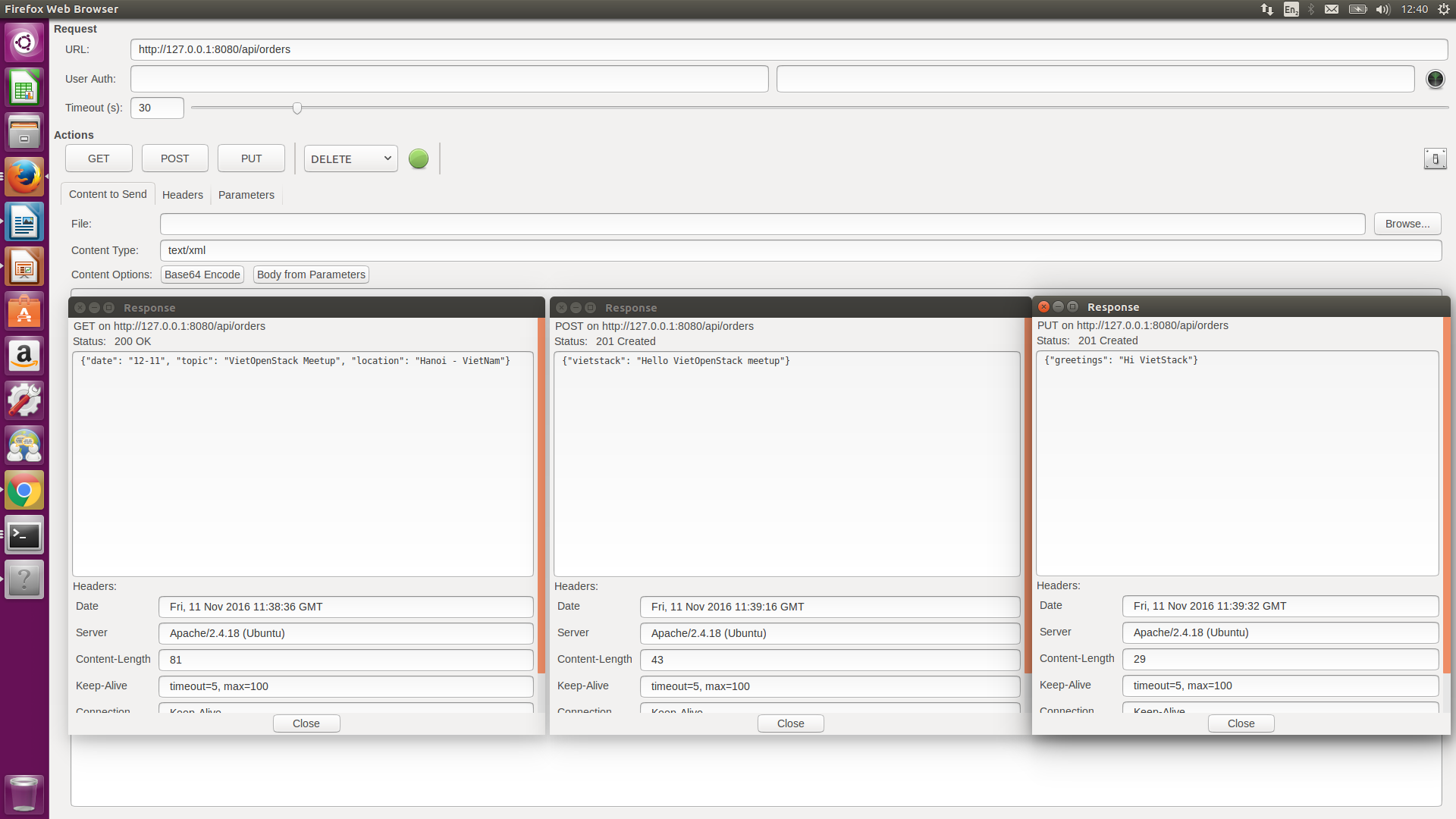
You can see the result of each action of GET/POST/PUT
Have fun!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!1
12/11/2016
VietStack team

Comments